The diagnostic medical imaging field is a very lucrative area of specialization. With the increasing demand for more specialists in the field of medicine, it’s not surprising that there are many options to choose from when deciding on a career pathway.
The field of radiological science alone has professions such as radiologist, sonographer, mammographer, and nuclear medicine technologist. Each makes vital input for adequate patient care.
In this post, we will be comparing a Radiologist Vs Sonographer, as both are fields in healthcare that have inter-related and often confusing roles.
So what are the differences between a radiologist and a sonographer? How are their careers structured? What does each job entail? And how much do they get paid?
Table of Contents
- Radiologist Vs Sonographer; Major Differences Between Them
- Radiologist Vs Sonographer Salary and Income
- Summary: What Is The Difference Between A Sonographer And A Radiologist?
Radiologist Vs Sonographer; Major Differences Between Them
A radiologist and a sonographer both have different jobs, but they work in the same field of medicine. The two careers are very similar, yet their duties vary.
So what is the difference between a Sonographer and a Radiologist? Below are some key differences between a Radiologist and a Sonographer.
Radiologist Doctor; Career, Education, Degree, and Jobs

Is A Radiologist A Doctor?
A Radiologist is a doctor that specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of illnesses through the use of medical imaging procedures like ultrasound, x-ray, computed tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography, and nuclear imaging techniques.
To become a Radiologist, you need 4 to 6 years of training in medical school depending on how many years medical school is in your country. Then another 4 to 6 years of residency training to become a medical specialist in the field of radiology.
How Many Years Does It Take To Become A Radiologist?
It takes a minimum of 13 years in college for Radiologists to complete their training and this includes the medical school training, residency program, and one to two years fellowship program. This is the required education to become a Radiologist.
What Radiologists Do; Radiology Jobs and Subspecialties
To understand better what radiologists do, then you must know the various subspecialties under this field of medicine. After the radiologists years of college training, they are still allowed to specialize in other subspecialties.
And some of these subspecialties are;
- Abdominal Imaging: These specialists are concerned with the imaging of the abdomen and the pelvic region. The imaging modality which they use is ultrasound, x-ray techniques including hysterosalpingography.
- Thoracic Imaging: Thoracic imaging is an imaging technique that is concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases affecting the chest and surrounding structures.
- Interventional Radiology: This is also known as Interventional Vascular Radiology. It is one of the subspecialties of radiology that deals with the use of ultrasound guidance to perform minimally invasive procedures. These procedures are done with the aim of diagnosing a disease or delivering treatment.
- Neuroradiology: This subspecialty of radiology involves the use of neuroimaging techniques to diagnose and characterize abnormalities affecting the central and peripheral nervous systems (the head and neck). Such Neuroimaging techniques include;
- Computed axial tomography
- Diffuse optical imaging
- Event-related optical signal
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Magnetoencephalography
- Positron Emission Tomography
- Single-photon emission computed tomography
- Cranial Ultrasound
- Functional Ultrasound Imaging
- Quantum Optically-pumped magnetometer
- Interventional Neuroradiology: This medical subspecialty cuts across different fields like Radiology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology. It is also known as Endovascular Surgical Neuroradiology, Neurointerventional Surgery, and Endovascular neurosurgery. Interventional neuroradiology involves the use of minimally invasive image-based technologies and procedures for the diagnoses and treatment of diseases affecting the head, neck, and spine.
- Pediatric Radiology: This is another subspecialty that cuts across Pediatrics and Radiology but this time, imaging techniques are used in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases affecting children.
- Nuclear Medicine: Nuclear medicine is a recent subspecialty in radiology and involves the use of radioactive elements and nuclear imaging techniques in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
- Emergency Radiology: This is a recent subspecialty in radiology that is concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of acute conditions. These specialties provide support to trauma surgeons in the management of critical illnesses requiring urgent attention.
- Breast Imaging and Women’s Imaging: This area of specialization in radiology involves all the imaging procedures that are used in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases affecting the breast and other organs peculiar to women.
- Radiation Oncology: These specially trained radiologists are concerned with developing and administering the best treatment plan to cancer patients based on the nature of the malignancy. Radio-oncologists are well trained in cancer medicine and they make use of radiation techniques to administer therapeutic doses of radiation to those body parts affected by cancer.
It is good to note that in recent times, most Radiology specialties are majorly concerned with the interpretation of films and imaging findings from simple imaging procedures like ultrasound and x-ray after the technicians (Radiographers and Sonographers) must have done the procedure.
But for more complex procedures like radiotherapy, neuroimaging, and interventional radiologic procedures, radiologists are actively involved in the process.
Sonography Degree, Program, Career and Job Descriptions
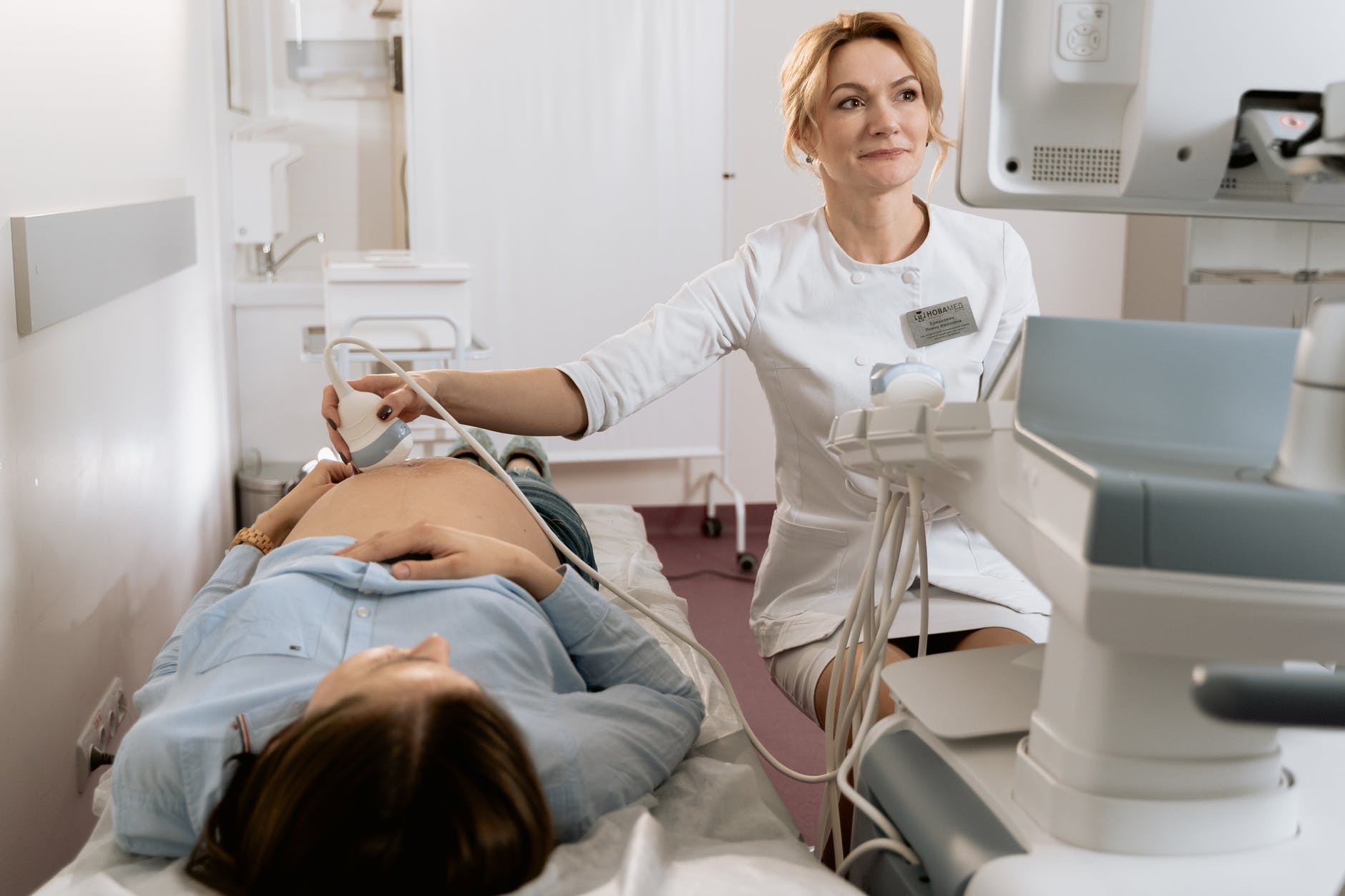
Who Is A Sonographer?
Sonography is a healthcare profession that involves the use of ultrasound imaging and ultrasonic imaging techniques and devices to make a diagnosis.
A sonographer is not a doctor, but to become one, you need to have a sonography degree in an accredited training center. These health scientists have grounded knowledge in ultrasound physics, human anatomy, physiology, and some pathology.
Sonography Program; Do You Need A Degree To Become A Sonographer?
Yes, a degree is needed to become a sonographer (Sonography degree).
There are different education programs and pathways for people who want to earn a sonography degree in different parts of the world.
There are also different subspecialties in sonography that one can specialize in after obtaining a sonography degree from a recognized sonography program. Some of the subspecialties in sonography include;
- General Sonography (registered under obstetric/gynecological and abdominal sonography).
- Cardiac sonography or Echocardiography
- Obstetrical Sonography
- Vascular sonography
- neurosonography
- Musculoskeletal Sonography
Sonographers in Australia receive their license from the Australian Sonographers Accreditation Registry (ASAR) after they must have completed a post-graduate ultrasound program in any of the accredited Australian Universities.
Sonographers In Canada also receive their training through an accredited sonography program either as a direct entry program for a degree, advanced diplomas, or second discipline graduate certificate program. To become a registered sonographer in Canada, you must pass the Canadian Clinical Skills Assessment.
To become a Sonographer in the United Kingdom, you receive training delivered as an MSc/PGDip/PGCert by any of the universities accredited by the Consortium for Accreditation of Sonographic Education. This means that to become a sonographer in the U.K, one needs at least a Bachelor’s Degree. Hence, the training will take nothing less than 4 years to complete.
Sonographers in the United States need a minimum of one and a half years to get a degree in diagnostic medical sonography. There are two major licensing bodies for a sonography degree in the united states; Cardiovascular Credentialing International and the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). Institutions that organize sonography programs in the US are accredited by the American National Standards Institute.
How Many Years Is The Sonography Degree?
Earning a sonography degree takes about one and half years to two years to complete.
But in addition to this, you will need to have completed a Bachelor’s degree in any of the health-related courses to join a sonography program.
Sonography Job Descriptions
A sonographer uses high-frequency sound waves to image the internal tissues and organs of the body. These high-frequency sound waves are called ultrasound and are completely harmless.
Below are the job descriptions and responsibilities of a sonographer;
- Counselling patients on the sonographic procedure they are about to undergo. This includes spelling out the risks, benefits and possible complications.
- Sonographers make sure that the images they take are clear enough to help a radiologist make a diagnosis.
- They select the adequate settings and configurations needed for a particular procedure and adjusts patients to a suitable posture for a better imaging.
- Sonographers ensure the safety and comfort of patients during sonographic procedures.
- A sonographer should be able to identify differences between normal and abnormal tissues in the body during imaging.
- They present the final result or sonograms to the radiologist or attending physician for report and diagnosis.
- They obtain and document the relevant medical history of patients for record keeping and research purposes.
- They also play a vital role in assisting radiologists and physicians during an invasive procedure.
- They ensure adequate maintenance of sonographic tools and equipment.
- A sonographer can perform simple non-invasive medical procedures like; administration of intranasal oxygen, vital sign monitoring like blood pressure measurement, and simple first aid.
- Sonographers should have excellent communication skill to communicate effectively with patients during sonographic procedures.
Radiologist Vs Sonographer Salary and Income
Both radiologists and sonographers all over the world earn a decent living and their jobs are quite satisfying when compared to many other medical specialties, surgical specialties, or health-related disciplines.
The next question is; who gets paid more radiologists or sonographers? Below is the average income of a sonographer and radiologist in the United States according to Ziprecruiter.
Radiologist Pay; How Much Does A Radiologist Get Paid?
How much radiologists make can be calculated by finding their hourly pay and multiplying it by the number of weeks, months, and years.
The average hourly pay of a radiologist is approximately $155.79/hour.
In a week, this is calculated as $6,232/week and $27,003/month.
Hence, the average annual salary of a radiographer is $324,036/year. But depending on your level of experience and your location, this can be as high as $400,000/year and as low as $80,500/year.
Sonographer Salary; How Much Sonographer Make A Year
The average hourly income of a sonographer in the United States ranges between $29.17/hour to $46.40/hour.
So in a year, an average sonographer earns between $60,677/year and $96,502/year. This is also largely influenced by your level of experience, location, and place of work.
Summary: What Is The Difference Between A Sonographer And A Radiologist?

Education and training program
A radiologist is a doctor who has completed 4 to 6 years in medical school, done an internship for one year, a residency program for 4 to 5 years, and one to two years of fellowship.
On the other hand, a sonographer is Bachelor’s degree holder who undergoes a one and half to two-year sonography program to become a licensed sonographer.
Technology
A radiologist uses different varieties of diagnostic and therapeutic imaging techniques in the management of patients. These imaging techniques include; magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography scan, positron emission tomography scan, ultrasound, nuclear imaging, etc.
But a sonographer is specially trained to use ultrasound imaging to take images of the internal tissues and organs of the human body. The result is further sent to a physician (usually a radiologist for interpretation and diagnosis).
Diagnosis and Treatment of Diseases
Since a radiologist is a doctor, he/she do not only make a diagnosis from imaging studies. But they also use imaging-guided procedures to deliver treatment to patients in the target organs affected by diseases in real-time. But a sonographer is neither trained to make a diagnosis nor deliver treatment.
Protection Levels
Since radiologists engage in some invasive procedures, some of which involve exposure to high energy radiations, they require more sophisticated personal protective gadgets during such procedures, unlike the sonographer.
You May Also Like:




